
Ms-9 Question bank (11)
Ms-9 Question bank
Ms-9 Dec 2007
Written by sales@mbaonlinepapers.com sales@mbaonlinepapers.comMS-9 Dec, 2007
MS-9 : Managerial economics
1. What is the basic objective of a firm ? Distinguish between 'Accounting Profit and 'Economic Profit' with the help of an illustration.
2. What do you understand by demand forecasting while describing the regression method of demand forecasting explain why it is important for the firm to forecast demand
3. Distinguish between the following with the help of illustrations :
(a) Fixed costs and Variable costs
(b) Short'run costs and Long-run costs
(c) Direct costs and Indirect costs
(d) Total cost, Average cost and Marginal cost
4. (a) Differentiate between Monopoly and Monopolistic competition giving examples
(b) Explain why profit is maximum at a level where MC = MR. Is profit always maximum when MC =MR ? Comment.
5. (a) What are the different types of statistical analyses used in the estimation of production function ? Explain briefly with the help of examples. Discuss the limitations of different types of statistical analysis.
(b) Briefly explain how the Cobb Douglas production function can be used to determine returns to scale.
6. (a) Which of the following commodities has most inelastic demand ? Give reasohs for your answer.
(i) Soap
(ii) Salt
(iii) Penicillin
(iv) Ice-cream
(v) Cigarettes
(b) Suppose the demand function of a product is given as
Q =500 - 5P. Find the profit maximising price when
i) MC:=0
ii) MC=20
7. Suppose you are a sales manager of an organization. Explain how does the analysis of demand contribute to business decision making, in the light of the responsibilities of a sales manager.
Ms-9 Dec 2008
Written by sales@mbaonlinepapers.com sales@mbaonlinepapers.comMS-9 Dec, 2008
MS-9 : Managerial economics
1. Explain the concept of price elasticity of demand and the relationship between price elasticity, total revenue and marginal revenue
2. Show graphical derivation of MP and AP curves from the total product function. Show also the three stages of production. What economic purpose do the stages
of production serve ?
3. Explain with examples economies and diseconomies of scale. How do economies and diseconomies of scale determine the shape of the LAC ?
4. Write notes on the following :
(a) The Equi Marginal Principle
(b) Elasticity of Substitution
(c) Linear Cost function
(d) Types of markets
5. (a) Under perfect competition average revenue equals average cost in the long run. Why do firms produce under such a condition ?
(b) A monopolist earns super normal profits even in the long run. Discuss
6. (a) Write True or False :
(i) In a firm's short-run production function, the firm's labour and plant are held
constant while its machinery is allowed to vary.
(ii) The law of diminishing returns is unrealistic because it implies that we could feed the world from our back garden.
(iii) The least-cost input combination producing a given level of output always be achieved in the short run.
(iv) The law of eventually diminishing returns describes a short run situation in which labour varies but fixed factors do not.
(v) The greater the cost of storing a good, the greater will be the gap in its price now and 2 years later.
(vi) Scale is a short-run concept.
(vii) When an input's average product exceeds its marginal product, average product is increasing.
(viii) The long-run average cost curve slopes downward over a range of output where a firm experiences a decreasing returns to scale.
(ix) Because consumers like variety, we cannot conclude that monopolistic competition is inefficient.
(x) The theory of the kinked demand curve does not predict the price where the kink will occur.
(b) The market demand function for a product sold by a monopolist is given below :
QD=2500-10P
The monopolist marginal cost function is :
MC=10+Q
Calculate the equilibrium price and quantity
Case study IBM
7. Read the following case and answer the questions given at the end.
LONG-RUN COSTS AT IBM
(LONG RUN COST FUNCTION)
The IBM Corporation is a leading manufacturer of electronic computers. Based on its internal memoranda, IBM's long-run total cost of producing various quantities of its Pisces (370/168) machines was as shown below :
For output levels in the relevant range, the equation
for this total cost function is
C = 28,303,800 + 460,800 Q,
where C is total cost (in dollars) and Q is the number of machines.
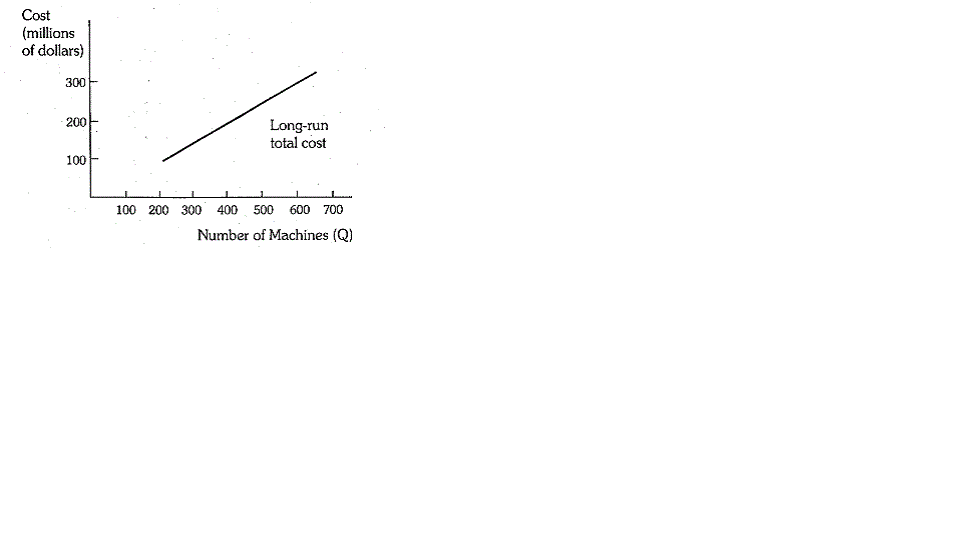
A) If the entire market for this type of machine is 1,000 machines, and if all firms have the same long-run total cost function, to what extent would a firm with 50 percent of the market have a cost advantage over a firm with 20 percent of the market ?
b) What is the long-run marginal cost of producing such a machine ? Does marginal cost depend on output ?
c) Do there appear to be economies of scale ?
d) The data presented above are forecasts of costs based largely on engineering data, not on historical record of actual costs. Why would IBM make such forecasts ? What factors might result in errors in these forecasts ?
Ms-9 Dec 2009
Written by sales@mbaonlinepapers.com sales@mbaonlinepapers.comMS-9 Dec, 2009
MS-9 : Managerial economics
1. Distinguish between profit maximisation and value maximisation giving examples.
2 (a) Briefly explain the concept of price elasticity of demand giving suitable examples.
(b) What are the determinants of price elasticity ? Explain giving examples.
3. Write short notes on the following giving suitable examples :
a) Breakeven output level
b) Profit contribution analysis
(c) Operating leverage
4. Critically comment on the factors which determine the nature of competition giving suitable examples.
5 (a) Why will managers prefer to operate in a cartel type environment as opposed to
competition ? Explain.
(b) Sustaining collusion is difficult for firms. Explain why, with reference to the prisoners dilemma.
6.You are given to understand that the existing firm in a market drives 80% of its revenues from 20% of its customers. Your boss wants you to develop a strategy to enter this market to compete with the existing firm (incumbent). Your answer should focus on :
a)How you would target existing customers ?
b) How you would seek to attract new customers ?
c) It is possible that the incumbent will also change his strategy following your decision
to enter. How according to you will the incumbent react ?
d) What will be your counter strategy to combat the incumbent ?
7. What do you understand by 'laws of production ? Explain the production function with one variable input highlighting the law of diminishing marginal returns and the stages of production
